1198
Farm Irrigation
题目描述
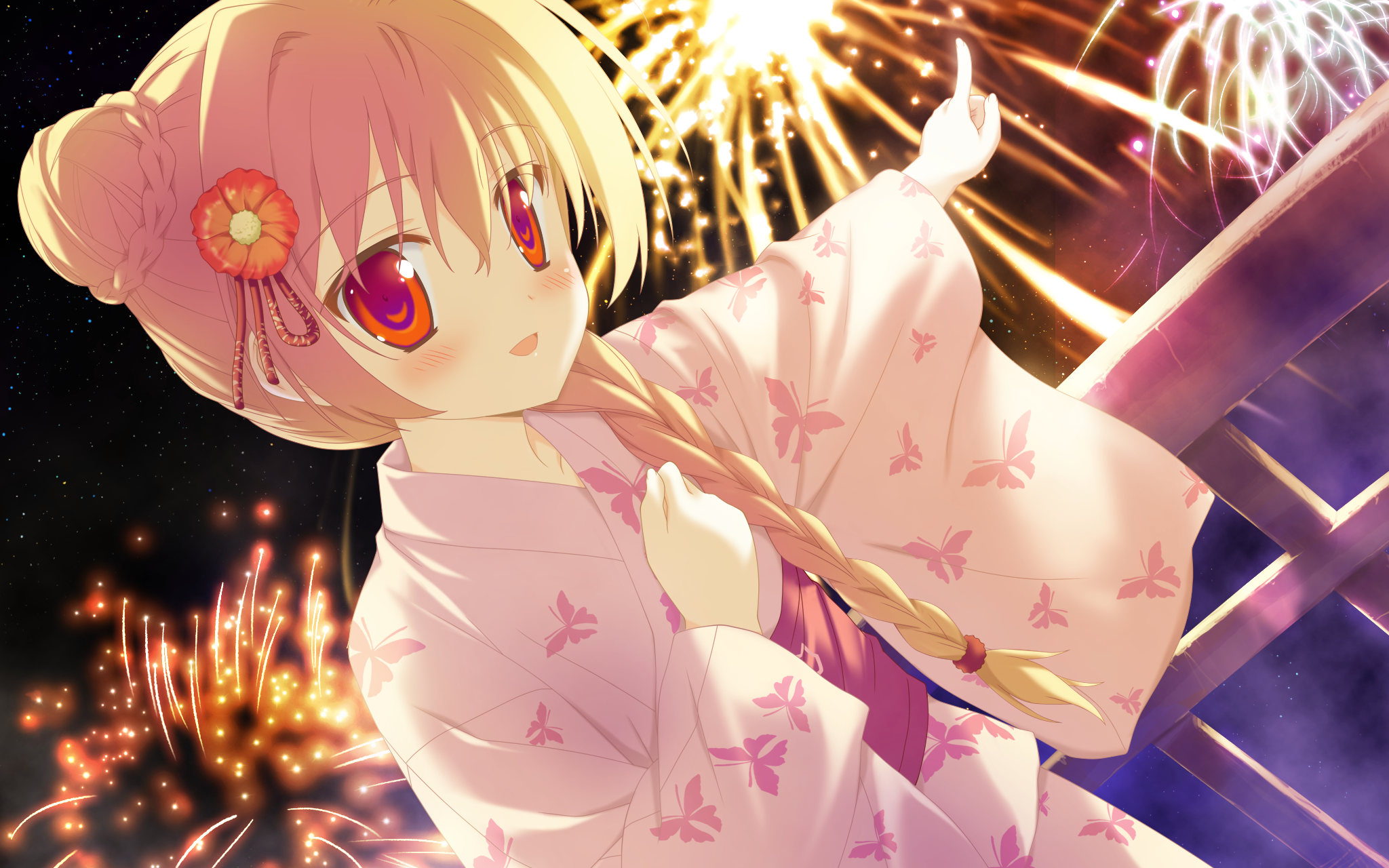
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
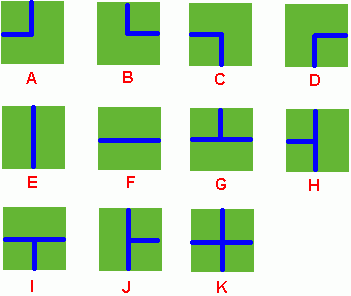
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like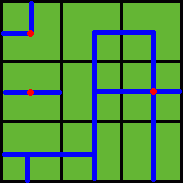
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
输入要求
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of ‘A’ to ‘K’, denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
输出要求
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
输入样本
2 2
DK
HF
3 3
ADC
FJK
IHE
-1 -1
输出样本
2
3
基本思路
情景抽象成并查集问题:试问能形成多少个树?
那么这些树的根结点的和就是井的数目。
并查集套路:初始化、查找、合并。
但是这一个个管道图怎么抽象成一个结点并使之能够与其他结点合并呢?
我们令管道图有水经过的为1,没有水的为0,从上面沿顺时针依次设置,比如A就是{1,0,0,1}。我们判断第一行的管道图的下面和对应下一行的管道图的上面都为1则可合并,同理,第一列的管道图的右边和对应下一列的左边都为1也可以合并。如此遍历,最后再判断根结点,计算其个数即可。
实现代码
1 |
|






